Cause
Gout starts suddenly, usually during the night, with a severe joint pain which is so strong that the slightest touch of the covers can cause extreme pain for the patient. It normally affects only one joint, usually that of the big toe.
The cause of the disease is linked to diet, that is, a higher intake of protein-rich foods such as rich meats, dairy, eggs, etc.
Treatment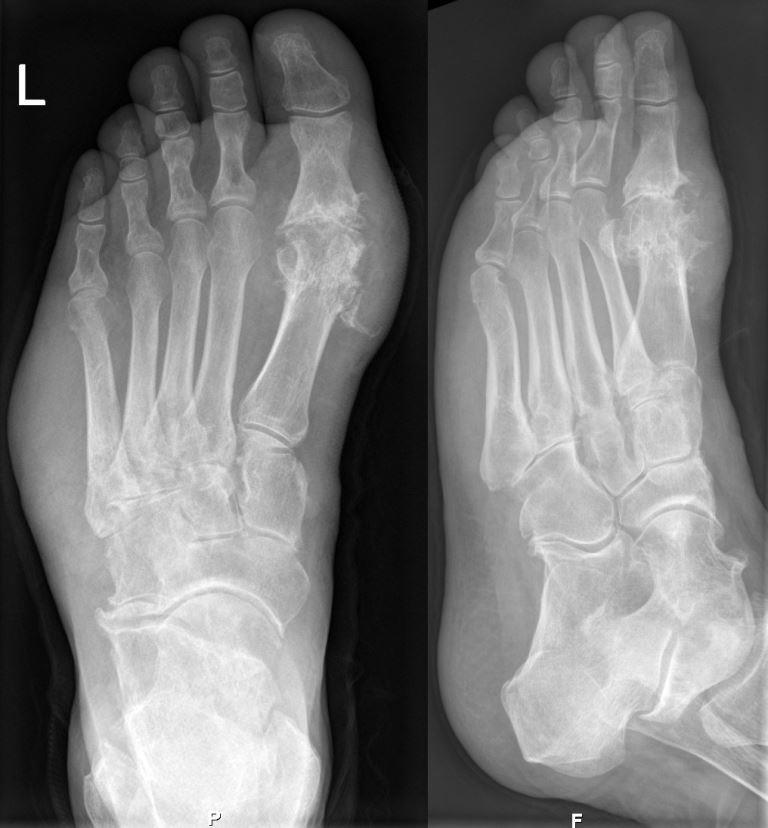
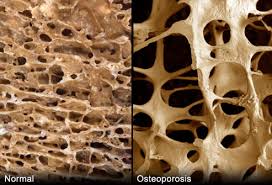
Cause
Osteoporosis most commonly occurs in post-menopausal women and then it is called primary osteoporosis. When osteoporosis is the result of other diseases or long-term use of medications that cause bone demineralization, it is called secondary osteoporosis. Senile osteoporosis occurs in both men and women over 75.
With osteoporosis it is important to diagnose the level of bone density (bone densitometry) on time and start treatment immediately.
Osteoporosis can be halted or slowed down with a proper regime, which entails:
Cause
Diabetic polyneuropathy is a disease of the peripheral nerves caused by diabetes.
The most common symptoms include burning sensations, pangs or tingling in the legs, especially the soles, intermittent or constant numbness, and feeling as if one is wearing socks or boots. There may be a constant burning sensation and severe pain and walking is often painful and described by patients as walking on “hot coals”. An intense shooting pain in the feet or legs can also occur.

Cause
It is a chronic, progressive, inflammatory disease of the skeletal system. First it affects the lumbar and sacroiliac region and then spreads to ligaments and connective tissue along the spine. The inflamed area then ossifies and the spine curves forwards and becomes rigid and immobile. The disease progresses in flares and gradually spreads to peripheral joints. Later there are changes to the eyes, heart, lungs and digestive organs. It takes 10 to 25 years to fully develop.

Cause
The disease occurs as a result of degenerative changes to the articular cartilage. In its place there appears a bony growth on the margin of the bone which reduces the mobility of the joint. This occurs in all the joints of the hand reducing the mobility of the fingers and the ability to grasp and hold objects. It does not affect the patient’s general health, but it makes their daily life extremely difficult.

Cause
The most common causes of reduced mobility are chronic inflammatory degenerative diseases. They occur with age reducing patients’ mobility, their ability to care for themselves as well as their independence and self-confidence.

Cause
The condition develops as a result of degenerative changes in articular cartilage. It affects all the peripheral joints (knees, hips, shoulders, fingers, foot bones), often several at once. The causes include microtraumas, joint overload, doing one-sided sports, obesity, badly healed fractures, deformities, muscle weakness and, on the other hand, genetics, age, unhealthy diet and reduced physical activity.

Cause
This condition is manifested by pain throughout the body. In addition to back muscle pain, the patient experiences morning stiffness, headaches, depression and fatigue, difficulty sleeping, numbness in hands and feet, restless legs and sensitivity to sound, light or temperature changes. It often occurs together with other conditions. Fibromyalgia more commonly affects women.
